A vacuum oven is a versatile piece of laboratory equipment commonly used for delicate heating and drying processes. They are commonly used when drying very small parts or when dealing with removing flammable solvents like methylated spirits or alcohol. The oven usually functions at a steady temperature of around 3600 °F to 4500 °F (2000 °C to 2500 °C). Read More…
Weiss Envirotronics is a worldwide leader in the design, manufacturer and service of environmental test chambers. A complete line of standard and custom chambers, from bench top models to full walk-in and drive-in solutions to meet any testing requirement. Not sure what you need? Let one of our applications engineers help. Weiss Envirotronics, Inc is ISO 9001 registered and A2LA accredited.

Complete finishing systems are designed around your specific process needs and are optimized to fit within your space requirements. We specialize in producing paint systems for wet and powder coatings, while also providing comprehensive design, fabrication, installation, start-up, and training services. Our complete finishing systems consist of an overhead conveyor, pretreatment washer, dry-off...

Surface Combustion offers a diverse product offering for batch, continuous furnace designs for atmosphere, non-atmosphere, or vacuum processing of ferrous and/or nonferrous components/materials. The convection design is optimal for temperatures between 350°F – 1400°F and are engineered to perform and built to last.
Since 1961, Thermal Engineering’s process & finishing systems contribute to the product quality of many automobile, furniture, paper, plastic & building products. Thermal’s industrial ovens offer savings in regards to time, energy & space and its solutions are designed for maximum flexibility for customers' use and with all applicable safety & code requirements that encompass a quality system.

Kleenair Products designs, engineers and manufactures high quality industrial ovens for industrial process systems. Our aging ovens, coloring ovens, drying ovens and food baking ovens serve many industries. We test fire each oven before shipping, guaranteeing your satisfaction. You will also find other process systems at Kleenair, including furnaces, drying systems, and energy recovery equipment.

C.A. Litzler Co. is ready to help you with your heat processing needs. With 60 years of designing and manufacturing experience, you can rest assured that the industrial oven you need can be built by us. We are determined to find the product that will meet your every need and requirement. Visit our website or give us a call today to learn more about how we can meet your needs.

More Vacuum Oven Manufacturers
What Is a Vacuum Oven?
A vacuum oven is a highly specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed for controlled heating, drying, and processing of materials under reduced atmospheric pressure. Unlike conventional drying ovens, vacuum ovens utilize a vacuum-sealed chamber to remove air and moisture, enabling even delicate and heat-sensitive materials to be processed without the risk of oxidation, contamination, or thermal degradation. This makes vacuum ovens indispensable in a wide range of industries, including pharmaceuticals, biotechnology, electronics manufacturing, medical device production, and materials science.
Vacuum ovens are especially effective for tasks requiring gentle drying, precise temperature control, and the safe removal of flammable solvents such as methylated spirits, ethanol, and other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). They are often used to dry very small parts, prepare sensitive samples, and process substances that could be damaged by exposure to air or high heat. Modern vacuum ovens typically operate within temperature ranges of 86 °F to 572 °F (30 °C to 300 °C), though some industrial vacuum ovens can achieve even higher settings for specialized applications.

How Do Vacuum Ovens Work?
Vacuum ovens operate by combining heat with a vacuum environment, drastically lowering the pressure inside the chamber. By reducing atmospheric pressure, the boiling points of water, solvents, and other volatile materials are lowered, allowing for effective drying and degassing at much lower temperatures than would otherwise be possible in a standard convection oven. This process both protects sensitive samples and ensures thorough removal of unwanted substances.
In practice, vacuum ovens are commonly used for:
- Drying laboratory glassware and instruments
- Degassing epoxies, resins, and adhesives
- Removing solvents from pharmaceutical compounds
- Outgassing electronics components and semiconductors
- Curing polymers and composite materials
- Drying botanical extracts and herbal samples
The key advantage of vacuum drying is the substantial reduction in oxidation and the prevention of chemical reactions with ambient air. This is critical in medical device manufacturing, electronics assembly, and food processing, where product purity and quality are paramount. Additionally, vacuum ovens help protect laboratory technicians and production staff by minimizing exposure to potentially harmful or toxic fumes.

The vacuum chamber is the heart of the oven. Once a sample is placed inside, the chamber is sealed and air is evacuated using a vacuum pump. Heat is applied via external or internal heating elements, and precise control systems ensure uniform temperature distribution. As pressure drops, the boiling point of contained liquids decreases, causing rapid evaporation and efficient moisture removal without the risk of burning or overheating the sample. This principle explains why water boils at lower temperatures at higher altitudes—a concept harnessed and controlled inside the vacuum oven.
Key Specifications of Vacuum Ovens
When selecting an industrial or laboratory vacuum oven, several critical specifications should be considered to ensure optimal performance for your specific application. These include:
- Temperature Range: Defines the minimum and maximum operating temperatures. Most laboratory vacuum ovens operate between 30 °C and 300 °C, but specialized models may accommodate higher ranges.
- Chamber Capacity: Indicates the internal volume of the oven, often measured in liters or cubic feet. Capacity requirements will depend on the size and quantity of materials to be processed.
- Vacuum Pressure Range: The achievable vacuum level (measured in torr, mbar, or pascal) is crucial. Common categories include:
- Rough vacuum: < 760 torr to > 1 torr
- Medium vacuum: < 1 torr to > 10-3 torr
- High vacuum: < 10-3 torr to > 10-8 torr
- Ultra-high vacuum: < 10-8 torr
- Material Construction: Stainless steel chambers are common for superior chemical resistance and durability.
- Control Interface: Digital microprocessors, programmable controllers, and touchscreens are available for advanced monitoring and automation.
- Safety Features: Over-temperature protection, vacuum relief valves, and alarms are vital for safe operation.
Searching for a vacuum oven with specific features? Consider the required chamber size, maximum achievable vacuum, temperature uniformity, and compatibility with your laboratory or production environment. Browse our vacuum oven manufacturers directory for detailed product specifications and expert guidance.
Types of Vacuum Ovens
Vacuum ovens come in several designs, each tailored to specific operational needs and industry requirements. The two most common types are electronic-controlled ovens and microprocessor-controlled ovens, but there are also custom vacuum ovens and walk-in vacuum ovens for large-scale applications.
Electronic Controlled Ovens
Electronic-controlled vacuum ovens utilize mechanical and analog controls to manage chamber temperature, pressure, and vacuum levels. These ovens typically feature:
- Enclosed heating elements for stabilized and uniform heat distribution
- Manual or dial-based controls for temperature, vacuum, and purge gas
- Front-facing control panels for easy operator access
- Backup systems to prevent overheating and ensure safe operation
- Gas and vacuum system connectors at the rear for introducing inert gases (like nitrogen or argon) and purging air from the chamber
- Observation windows for real-time process monitoring

These ovens are ideal for straightforward drying, curing, and degassing applications where precise digital control is not required. They are popular in research laboratories, quality control departments, and general industrial settings.
Microprocessor Controlled Ovens
Microprocessor-controlled vacuum ovens provide advanced digital control, automation, and process monitoring. These units are equipped with:
- Programmable temperature and vacuum profiles for complex drying and curing cycles
- Self-diagnostic features and system health indicators
- Thermostatic control for precise temperature stability
- Over-temperature and over-pressure alarms for enhanced safety
- Touchscreen or digital interfaces for intuitive operation
- Data logging and connectivity options for process validation and traceability

Microprocessor-controlled vacuum ovens are the go-to solution for users demanding maximum precision, repeatability, and process documentation. They are widely used in regulated industries such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, biotechnology, aerospace, and electronics production, where process validation and documentation are critical.
Custom and Industrial Vacuum Ovens
For large-scale manufacturing or unique research requirements, custom-designed vacuum ovens and walk-in vacuum ovens are available. These can be tailored to meet specific size, temperature, and vacuum specifications, and may include features such as multi-zone heating, automated loading systems, and integration with factory automation solutions. If you need a vacuum oven for pilot plants, bulk material drying, or large composite curing, consult with a specialist manufacturer for a turnkey solution.
Applications of Vacuum Ovens
Vacuum ovens are relied upon in a broad array of scientific, industrial, and manufacturing settings. Their ability to deliver controlled, uniform drying and processing under vacuum makes them invaluable for:
- Pharmaceutical manufacturing: Drying powders, granules, and sterile components
- Medical device production: Sterilizing and drying sensitive equipment and assemblies
- Electronics and semiconductor fabrication: Outgassing, curing, and moisture removal from PCBs, wafers, and assemblies
- Botanical extraction: Removing residual solvents from herbal extracts, cannabis concentrates, and essential oils
- Rubber and polymer processing: Curing, drying, and degassing elastomers, adhesives, and resins
- Food industry: Freeze-drying, dehydration, and packaging of sensitive ingredients
- Research and materials science: Controlled experiments on powders, ceramics, and nanomaterials

Wondering which vacuum oven is best for your application? Explore our in-depth Vacuum Ovens Buyer’s Guide to compare models, features, and industry-specific solutions.
Benefits of Using a Vacuum Oven
Vacuum ovens offer several notable advantages over conventional drying and curing equipment:
- Lower drying temperatures: Safely dry heat-sensitive or volatile samples without decomposition or loss of product quality.
- Faster drying rates: Reduced pressure dramatically accelerates solvent and moisture removal, improving productivity and throughput.
- Minimal oxidation and contamination: The vacuum environment prevents unwanted chemical reactions with air, ensuring sample purity and stabilizing sensitive materials.
- Gentle and uniform heating: Protects delicate samples, thin films, powders, and small parts from thermal damage.
- Enhanced safety: Lowers the risk of fire, explosion, or toxic fume exposure when drying flammable solvents or hazardous materials.
- Precision control: Advanced microprocessor-controlled ovens allow tight regulation of temperature and vacuum profiles, ideal for critical production processes.
Vacuum ovens are also essential for tasks that require regulatory compliance with standards such as GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice), ISO (International Organization for Standardization), and FDA (U.S. Food and Drug Administration) guidelines, especially in pharmaceutical, biotechnology, and medical device industries.
How to Choose the Right Vacuum Oven for Your Laboratory or Production Facility
Choosing the ideal vacuum oven involves assessing your specific requirements and matching them to the technical features offered by leading manufacturers. Consider the following decision factors:
- Sample size and throughput: Estimate the typical load and batch volume to determine the necessary chamber capacity.
- Temperature and vacuum requirements: Identify the temperature range and vacuum levels needed for your processes.
- Material compatibility: Ensure oven construction materials are compatible with the solvents, chemicals, or samples you process.
- Control options: Decide whether manual, digital, or programmable controls are best for your workflow and regulatory environment.
- Safety features: Evaluate the need for over-temperature protection, alarms, and vacuum relief mechanisms.
- Budget and total cost of ownership: Factor in not only the purchase price, but also maintenance, calibration, and energy consumption.
- Industry standards and certifications: Verify compliance with GMP, ISO, or other regulatory guidelines as required.
Looking for help choosing a vacuum oven? Contact our vacuum oven experts for personalized recommendations based on your application and industry.
Vacuum Oven Accessories and Upgrades
Enhance the performance and versatility of your vacuum oven with a range of accessories and optional upgrades, such as:
- Vacuum pumps: Rotary vane, diaphragm, or scroll pumps matched to required vacuum levels
- Shelves and trays: Adjustable, removable, or perforated shelves for optimal sample placement
- Inert gas purge systems: For applications requiring controlled atmospheres
- Data logging and remote monitoring: Integration with LIMS (Laboratory Information Management Systems) and networked control systems
- Custom chamber liners or coatings: For highly corrosive or reactive materials
- Calibration and validation services: Ensure accuracy and compliance with industry standards
Curious about which vacuum oven accessories are right for you? Browse our Vacuum Oven Accessories Guide for detailed information.
Buying Tips: How to Select a Vacuum Oven Manufacturer
To ensure you receive the best vacuum oven for your needs, it's important to compare multiple suppliers and evaluate their expertise, product range, and customer support. Use our directory of vacuum oven manufacturers to:
- Review business profiles highlighting technical capabilities and industry experience
- Access product datasheets, case studies, and application notes
- Use our patented website previewer to quickly compare offerings
- Contact manufacturers directly with questions or requests for quotes using our streamlined RFQ form
- Request references or customer testimonials to evaluate product reliability and support
- Verify after-sales service, warranty options, and maintenance agreements
Are you ready to request quotes or schedule a demo? Reach out to top vacuum oven suppliers today to get started.
Frequently Asked Questions About Vacuum Ovens
- What is the difference between a vacuum oven and a drying oven?
Vacuum ovens operate under reduced pressure, allowing lower drying temperatures and minimizing oxidation—ideal for sensitive samples. Standard drying ovens rely on convection and ambient pressure. - Which vacuum pump should I use with my vacuum oven?
The right vacuum pump depends on the required vacuum level, sample type, and process speed. Rotary vane pumps are common for general use, while diaphragm pumps are preferred for solvent-sensitive applications. - How do I clean and maintain a vacuum oven?
Regular cleaning with non-abrasive solutions, routine gasket inspection, and annual calibration help ensure optimal oven performance and longevity. - Can a vacuum oven be used for solvent recovery?
Yes. Many models allow for the safe collection of evaporated solvents, improving safety and reducing waste in pharmaceutical and botanical extraction processes. - How do I validate a vacuum oven for pharmaceutical use?
Validation typically involves installation qualification (IQ), operational qualification (OQ), and performance qualification (PQ) in accordance with GMP and regulatory guidelines.
Learn More and Get Expert Support
Whether you’re searching for a laboratory vacuum oven for research, an industrial vacuum oven for manufacturing, or need custom solutions for regulated environments, our team can help. Explore our comprehensive guides, product comparisons, and supplier network to make an informed purchasing decision. Don’t hesitate to contact us for expert advice, application support, or a personalized quote.









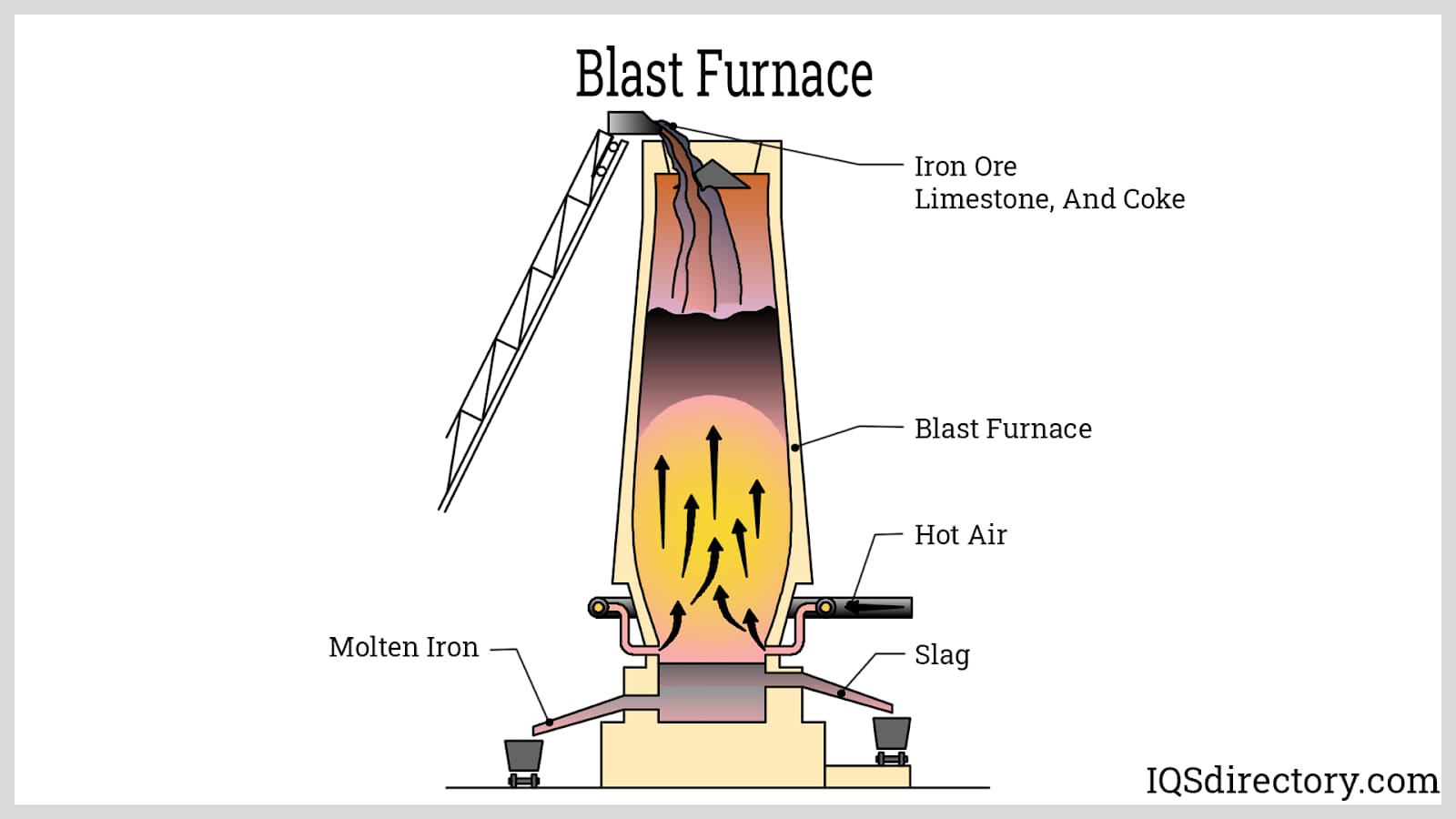
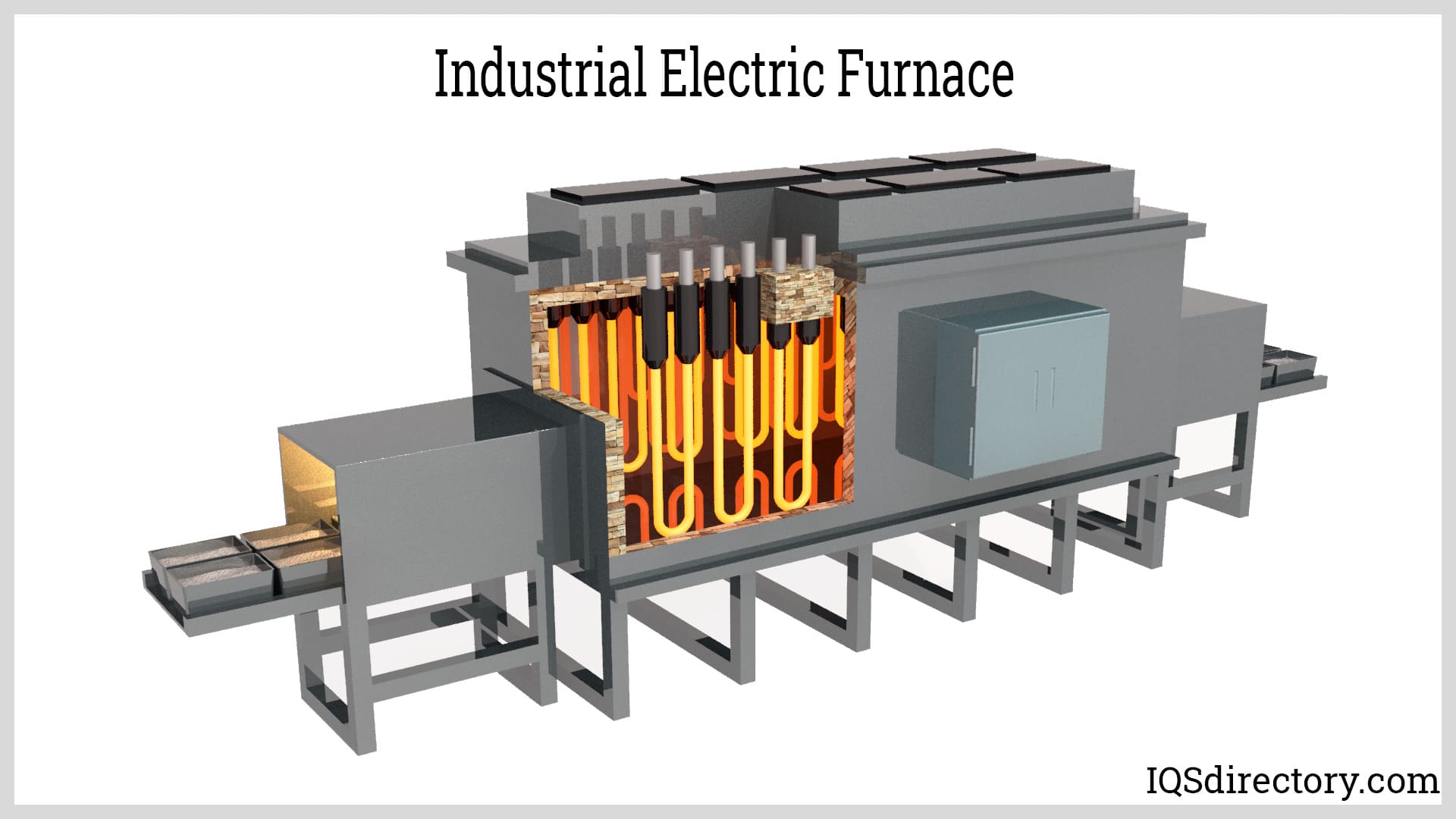

 Electric Heaters
Electric Heaters Industrial Dryers
Industrial Dryers Industrial Mixers
Industrial Mixers Industrial Ovens
Industrial Ovens Pressure Vessels
Pressure Vessels Pulverizers
Pulverizers Vibratory Feeders
Vibratory Feeders AGV
AGV Air Pollution Control
Air Pollution Control Assembly Machinery
Assembly Machinery Blowers
Blowers Conveyors
Conveyors Cranes
Cranes Deburring Machinery
Deburring Machinery Dust Collectors
Dust Collectors Heaters
Heaters Hose Reels
Hose Reels Lubricators
Lubricators Mezzanines
Mezzanines Modular Buildings
Modular Buildings Storage Racks
Storage Racks Ultrasonic Cleaners
Ultrasonic Cleaners Work Benches
Work Benches